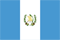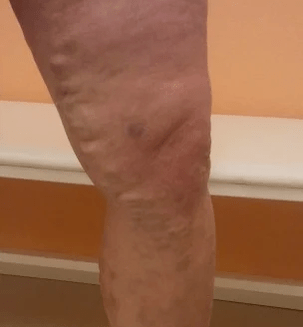
Varicose veins - This is the enlargement of the subcutaneous veins by more than 3 mm in diameter.Varicose veins develop due to decreased venous valves and weakness of the venous wall;At the same time, blood flow from the lower extremities, increased pressure inside the vein, which can lead to chronic venous insufficiency.
Sometimes, telanggiectasia and reticular veins are mistaken for varicose veins.
These are veins in diameter 3 mm and less, They do not affect venous drainage, but cause a clear cosmetic defect.
What is the prevalence of varicose veins?
Varicose enlargement of the subcutaneous veins occurs in 30 % of women and 15 % of male sexual age.The prevalence of varicose veins of the lower extremities increases significantly with age and is represented in people older than 60 years of age.The share of patients with trophic disorders in adulthood accounts for only 1.8%, and in old age the indicator reaches 20%.At the same time, all fifth patients in their lives are faced with thrombophilets.Among the causes leading to disability, the proportion of forms of vein disability forms is greater than the arteries.
The main risk factors for the development of varicose veins are:
- Older age
- A female sex
- Pregnancy
- Hormonal disorders
- A Positive Family History
Additional Risk Factors:
- Smoke
- Arterial hypertension
- Constipation
Literature on additional risk factors is contradictory.Moreover, the risk of developing venous disease is low.
How do varicose veins appear?

The most common manifestation is unevenly diluted veins that are above the surface.In some cases, they may be barely noticeable or only to be touched by the touch, in some they take the form of elimination by forming the nodes or resembling a large bouquet of grapes.
Often varicose veins are accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Feeling and tension in the legs
- Pain and/or hurts along the veins
- The rapid fatigue of the feet
- Itching of the skin of the feet
Rarely varicose disease can cause restless feet syndrome and leg cramps at night.
What are the dangers of progressing varicose veins?
In the absence of treatment, progression of varicose veins can lead to chronic venous insufficiency (CVN).The presence of HVN indicates severe disorders of lymphatic venous return (C3-C6 CEP classification of clinical classes), which include: chronic edema (lymphedema), skin color change (hyperpigmentation), venous eczema, skin contraction, trophic venous ulcer.
What are the complications of varicose veins?
The formation of thromboflebitis-thrombus in the superficial venous system is an event in front of which 20%of patients with varicose veins stand.Such thrombosis is accompanied by severe pain, redness of the skin, sealing the lower leg and/or thigh along the vein.In the absence of treatment, thrombotic masses are possible in the deep venous system.
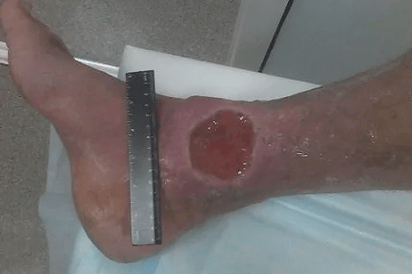
Deep vein thrombosis (TGV) - In most cases, the beginning of the process is asymptomatic.When thrombosis extends to the female segment and pelvic bone, the main blood flow from the lower extremities is accompanied by severe edema and pain syndrome and treated as a life -threatening situation.
Pulmonary arteries of thromboembolism (tela) - In 10% of cases, thrombotic masses in the deep veins of the lower extremities are fragmented and passed into the pulmonary arteries with blood flow, causing mortality.
What is needed for a correct diagnosis?
Given the diversity of vein diseases, all the details of the history of the disease and the history of the patient's life, the presence of concomitant diseases, the transactions, the result of an external examination by the physician, and the most important thing are ultrasound, ultrasound, ultrasound scanning, the correct diagnosis is important.The latter, today, is the most informative and non -invasive method of studying the veins of the lower extremities.
Varicose veins treatment, the most common methods:
- Medications treated with drug addiction have proven their effectiveness to reduce the symptoms of varicose veins, but they are unable to eliminate varicose veins.Pharmacotherapy has been successfully used to prevent complications in risk groups, pre -operative training and post -operative rehabilitation.
- Treatment of compression - Wearing special medical knitting clothing in the form of golf, stock, underwear.In some cases, a versatile bandage is used with elastic bandages of various expansion and pneumatic compression of the machines.The role of compression treatment is difficult to exaggerate, it is found at almost all stages of chronic vein prevention and treatment.
- Introduction of the drug vein lumen, which can cause its closure.This method is a gold standard to eliminate reticular veins.It is successfully used to treat not large diameter varicose veins and has restrictions on the elimination of abnormal subcutaneous veins.
- Classic Operation - Combined phlebectomy, modern performance is performed underpatient based on spinal or local anesthesia.In some cases, this is the only possible way when the target veins are very convincing and/or have a high extension.However, the method is trusted by the traumatic blood vessel procedures.
- Endo venous laser castle - The method of treatment for varicose veins in which the vein is not removed, but is closed from the inside with the energy of laser radiation, which directly inserts into the wholesale vessels with the fiber.The effectiveness of the procedure is compared to the results of the surgical removal of the vein, at the same time, characterized by minimal trauma.Rehabilitation time is 1-3 days.
- Radio Frequency Castle - A progressive way to eliminate abnormal blood flow to the trunk subcutaneous veins.This is a completely outpatient procedure performed under local anesthesia.The efficacy of treatment corresponds to the level of classic phlebectomy, pain syndrome is minimal or non -existent.Rehabilitation time is 1-2 days.